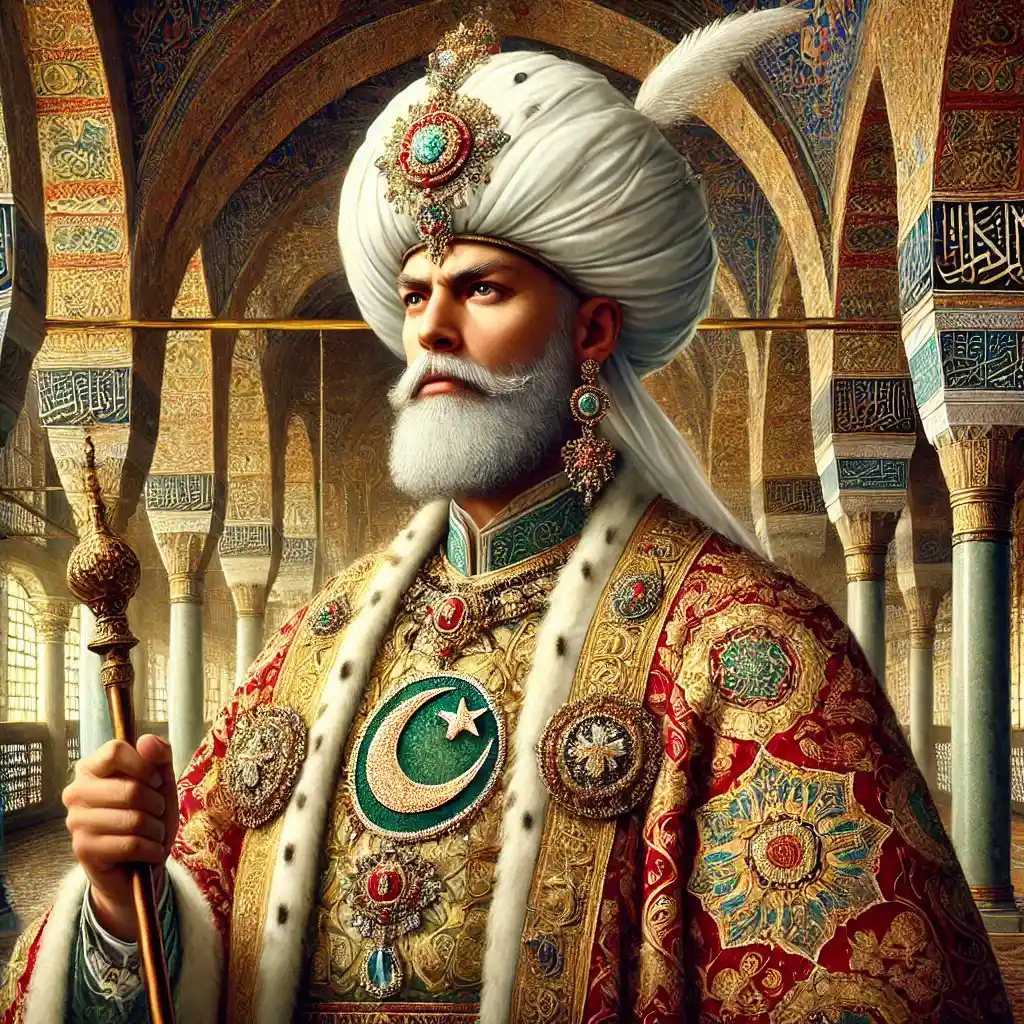
Osmanlı İmparatorluğu'nun altıncı padişahı olan II. Murad, 1421-1451 yılları arasında iki farklı dönemde tahtta bulunmuştur. Babası I. Mehmed’in ardından tahta geçen II. Murad, Osmanlı’yı yeniden güçlendirerek özellikle Balkanlar ve Anadolu’da önemli kazanımlar elde etmiştir. Aynı zamanda oğlu Fatih Sultan Mehmed’in yetişmesinde büyük bir rol oynayan bu hükümdar, Osmanlı Devleti’nin kurumsal yapısının pekişmesini sağlamıştır. Şimdi, II. Murad’ın hayatını ve Osmanlı tarihindeki etkisini inceleyelim.
II. Murad, also known as Murad II, was the sixth Sultan of the Ottoman Empire, ruling between 1421 and 1451 with a brief abdication in 1444. Born in 1404 in Amasya, he was the son of Sultan Mehmed I and Emine Hatun. II. Murad's reign was marked by significant military campaigns in the Balkans and Anatolia, administrative reforms, and cultural advancements. As the father of Mehmed the Conqueror, he played a pivotal role in shaping the future of the empire. His leadership was defined by resilience, vision, and a commitment to stabilizing and expanding the Ottoman state.
Early Life and Background
Birth and Lineage
Born in 1404, II. Murad was a member of the emerging Ottoman dynasty that was still consolidating its power in Anatolia and the Balkans. His father, Mehmed I, was instrumental in ending the Ottoman Interregnum and reestablishing central authority. His mother, Emine Hatun, came from a noble lineage, and her influence was significant in his early upbringing.
Education and Training
As a young prince, II. Murad was given a rigorous education that emphasized governance, military strategy, and Islamic jurisprudence. Tutors and advisors prepared him for the complexities of leadership, instilling in him a strong sense of duty and responsibility.
Role as a Governor
Before ascending the throne, II. Murad served as a governor in Anatolia, where he gained firsthand experience in administration and military command. This period was crucial in shaping his leadership style and understanding the challenges of ruling a diverse empire.
Political Climate of the Era
The early 15th century was a time of both opportunity and threat for the Ottomans. While the empire was expanding, it also faced challenges from rival Anatolian beyliks and European powers, particularly in the Balkans.
Accession to the Throne
Following the death of Mehmed I in 1421, II. Murad ascended the throne at the age of 17. His early years as Sultan were marked by efforts to consolidate power and respond to internal and external threats.
Military Campaigns
Balkan Conquests
II. Murad devoted much of his reign to expanding Ottoman influence in the Balkans. He led successful campaigns against Serbia, Hungary, and other European states, solidifying Ottoman control in the region.
The Siege of Thessaloniki
In 1430, II. Murad captured Thessaloniki, a strategically significant city that further strengthened Ottoman dominance in southeastern Europe. This victory demonstrated his military prowess and strategic vision.
The Crusade of Varna
One of the most notable events of his reign was the Crusade of Varna in 1444. Despite abdicating in favor of his son Mehmed II, II. Murad returned to lead the Ottoman forces, decisively defeating the Christian coalition.
Conflicts in Anatolia
In addition to his campaigns in the Balkans, II. Murad focused on consolidating Ottoman control in Anatolia. He subdued rival beyliks and reinforced Ottoman authority in the region.
Military Innovations
Under II. Murad, the Ottoman military adopted new technologies and tactics, including the increased use of gunpowder weaponry and the expansion of the Janissary corps.
Administrative Reforms
Centralization of Power
II. Murad implemented policies to centralize authority and reduce the power of local governors. This helped to strengthen the Sultan’s control over the empire.
Economic Policies
Recognizing the importance of economic stability, he introduced measures to promote trade and agriculture. These policies ensured a steady revenue flow and supported the empire’s military campaigns.
Judicial Reforms
To ensure justice across the empire, II. Murad reformed the legal system, appointing qualified judges and establishing clear legal codes.
Cultural Patronage
A patron of the arts and sciences, II. Murad supported scholars, poets, and architects. His reign saw the construction of significant architectural projects, including mosques and madrasas.
Integration of Diverse Populations
II. Murad adopted policies that promoted the integration of diverse ethnic and religious groups within the empire. This approach fostered loyalty and stability.
Legacy and Historical Significance
Preparation of Mehmed the Conqueror
One of II. Murad’s most enduring contributions was his role in preparing his son, Mehmed II, for leadership. His mentorship laid the groundwork for Mehmed’s eventual conquest of Constantinople.
Contributions to Ottoman Stability
Through his military and administrative efforts, II. Murad ensured the stability and continuity of the Ottoman state during a critical period in its history.
Cultural Advancements
His support for culture and education enriched Ottoman society and left a lasting legacy that continued to flourish under his successors.
Historians’ Perspective
Historians regard II. Murad as a pragmatic and resilient leader who skillfully balanced military ambition with administrative efficiency.
Lessons from His Reign
II. Murad’s reign offers valuable lessons in leadership, particularly in navigating challenges and laying the foundation for future success.
Iı. Murad İngilizce Biyografisi
"II. Murad İngilizce Biyografisi" başlığı altında, Osmanlı İmparatorluğu’nun altıncı padişahı olan II. Murad’ın hayatı ve hükümdarlığı detaylı bir şekilde ele alındı. Onun liderliği, Osmanlı’nın Balkanlar ve Anadolu’daki gücünü artırmış, kurumsal yapıyı sağlamlaştırmış ve gelecek nesillerin başarısına zemin hazırlamıştır.
Summary: A Visionary Leader in Ottoman History
- II. Murad (1404-1451) was the sixth Ottoman Sultan, known for his military campaigns and administrative reforms.
- His reign solidified Ottoman control in the Balkans and Anatolia.
- He played a key role in preparing his son, Mehmed II, for future leadership.
- II. Murad’s policies promoted economic growth, legal reform, and cultural enrichment.
- The Siege of Thessaloniki and the Crusade of Varna were major milestones of his reign.
- His abdication and return to power highlighted his resilience and dedication to the empire.
- Historians recognize him as a stabilizing force during a critical period in Ottoman history.
- II. Murad’s legacy laid the foundation for the empire’s eventual golden age.